Digitization of Image Manuscripts--Scanning (3)
4 scanning process
1) Scanner preparation
Before using the scanner, check that the scanner's cable is connected. After the inspection is completed, turn on the scanner, wait until the scanner is stable, and then turn on the computer. In order to ensure the stability of the scanning quality, at least the scanner should be allowed to warm up for a period of time before use, in order to obtain better lighting conditions and a more ideal tone range.
2) Manuscript preparation
Before the image scanning, according to the characteristics of the image reproduction, the type, content, color, gradation, and definition of the original document shall be comprehensively examined to determine the process parameters that are consistent with the purpose of copying, the content of the original document, and the artistic reproducibility, and then the printed document shall be formed flat. Place it cleanly on the scanner's original holder.
3) Scan parameter settings
Cover the back cover of the scanner so that the printed original is in close contact with the original holder. Then activate the scan software and set the scan parameters. The scanning parameters include: selecting the original type (transmission, reflection, etc.), selecting the scanning image mode (RGB color mode, CMYK color mode, grayscale mode, etc.).
4) Image Prescan
Image prescanning refers to previewing an image at a low resolution to determine the area for fine scanning and setting the color.
5) Resolution setting
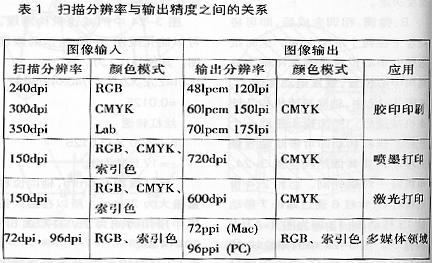
After the pre-scanning, you can set the scan area manually or automatically to determine the size of the image, and then set the scan resolution. The scan resolution setting of the image depends on the output of the image. The scan resolution of the print image = magnification × number of screens × quality factor. The quality factor is usually between 1.5 and 2 (if the output screen is less than or equal to 133 lpi. The quality factor takes a value of 2, and if the number of output lines exceeds 133 lpi, the quality factor takes a value of 1.5). Table 1 lists the relationship between the scanning resolution and the output resolution of images for different purposes.
The scanning resolution of linework depends on the target software or output device. If the scanned linework still needs vector software to depict it as a vectorized image, the scanning resolution is set to the highest optical resolution when the original is scanned; if the scanned linework is directly output, the original is scanned, the scanning is resolved. The rate should match the device output resolution. Scan Resolution = Output Device Resolution x Scaling Ratio, for example: Prepare a printer with a resolution of 600 dpi to print out a scanned original. The scanner's input resolution should be set to 600 dpi. The factors affecting the quality of the line scan include zoom ratio, output resolution, sharpness, black and white threshold, and so on.
6) Color and Level Settings
By setting the scanning parameters, the color and gradation of the image are adjusted, so that the scanned image is closer to the original, and the lack of the original can be compensated. The color and gradation settings include: black and white field calibration, gamma determination, and color balance settings. Black and white field scaling, also called scaling of highlights and shadows, refers to the tonal values ​​of the darkest and brightest points of an image while keeping the details constant. The selection of high light spots and dark spots can significantly change the effect of image copying. If the high light spot is set too low, the overall copy image density increases and the entire image darkens; otherwise, the image becomes lighter. The black and white field calibration of the image also takes into account the type of press and the properties of the printing paper. Table 2 shows the black and white field calibration used for several different printer/printing papers.
The main function of the gamma coefficient is to adjust the midtone of the image by adjusting the slope of the copy curve. Adjusting the gamma coefficient during the scanning process helps to compensate for image desensitization and hemiplegia due to underexposure or overexposure, and it can also By means of adjusting the gamma, the detail and contrast of the original image, mainly highlights or shadows, are enhanced. For luminosity dominated and underexposed images, the gamma ratio is generally adjusted to 1.8 to 1.9; for darker and predominantly overexposed images, the gamma is generally adjusted to 1.2 to 1.3; for normal images, the gamma is generally adjusted. It is 1.5 to 1.6. The color balance setting is usually to call a specific color characteristic curve. For example, people have set a series of ICC characteristic curves for different output media during scanning and debugging, so that they can be called in a later scanning job. In addition, the scanning software also provides some basic color correction methods: hue saturation adjustment, color balance adjustment, tone curve adjustment and so on.

7) Sharpness and network setting
The sharpness emphasis function is designed to compensate for the optical loss during scanning. By increasing the contrast of the edges of the image or adjacent areas of different color bars to highlight the image details, we can set high, medium, and low degrees of different levels according to the different types of originals. Sharpness emphasizes. Most scanning software provides sharp filters and USM filters. The sharp filter only increases the contrast of the whole image, while the USM filter only increases the contrast of the edges and maintains a high contrast between adjacent pixels of the edge.
The network setting function is mainly used for scanners to scan originals of printed matter. If the printed matter is used as originals, no processing is performed during scanning, and images are added to the screen when outputting. There are regular dot network information superimposed with moire, and the net setting function is set. For this purpose, the scanner's hardware adjustment or software algorithm is used to remove the original dot information so as to avoid the occurrence of dot moiré at output. For example: filters provided by the scanning software, such as blurring, noise introduction, etc. are available.
8) Fine scan
When all preparations and settings have been completed, it is ready for a formal scan. After the scan, if there is insufficient image, a series of post-processing must be performed: for example, further cropping the image, adjusting the size and image resolution of the image; further adjusting the color, the level, and the sharpness of the image; using a trimming tool to eliminate the layout Scratches and so on. Next select the appropriate file format to store the image.
Source: "Printing World"
Author: Huwei You German printing training center
Silicone pot holders are made up of silicone. It's low taint materials that have become an important kitchen tool. Silicone pot holders can withstand high temperatures, so they don`t get hot while you move pots and pans from ovens and stoves to counter tops or tables. They do not break down when exposed to heat. If hot pots and pans need to place on your kitchen table or stove, just place the pot holders beneath them. Table mat would protect the wood from the heat and safeguard the texture of your counter tops. Hot pads' ability to retain shape despite heat makes for superior trivets.
Pot Holder,Silicone Pot Holder,Non-Slip Silicone Pot Holder,Rubber Pot Holder
Yangjiang Superwins Trade Co., Ltd. , http://www.superwins-kitchenware.com