Computer Graphic Design and Prepress Graphic Processing 500 Q (1-4)
1. When making a plate, the original should be divided into four colors: blue (C), magenta (M), yellow (Y), and black (K). What is the color separation principle?
A: There are tens of thousands of colors on the screen in color drawings or color images. It is almost impossible to print all these thousands of colors in a single color. The method used for printing is four-color printing. That is, the original is first color-coded and divided into four color versions of blue (C), magenta (M), yellow (Y), and black (K), and then printed. Synthesis. The so-called "separation" is based on the principle of subtractive color, the use of red, green, and blue color filters for selective absorption of different wavelengths of color light features, and the original is decomposed into yellow, goods, blue three primary colors. In the color separation process, the color light absorbed by the color filter is the complementary color light of the color filter itself, so that a black and white image negative film is formed on the photographic film, and then the screen is screened again to form a dot negative film, and the copy is finally printed and colored into various colors. Printing plate. This is the earliest photographic separation principle.
Due to the development of printing technology, we can now separate, sample, and convert the color of a manuscript into digital information by using a prepress scanning device. That is, the color of the manuscript is divided into red (R) and green (G) by the same method as photolithography. Blue (B) three colors, and digitization, and then use a computer to mathematically decompose the digital information into blue (C), magenta (M); yellow (Y), black (K) four-color information.
2. Why should prepress images be screened?
A: Because the printing process determines that the printing can only use the dots to reproduce the continuous leveling of the original. If you enlarge the printed image, you will find that it is composed of countless dots of different sizes. We see that dot size is different, but all occupy the same size of the spatial position. This is because once the original image is screened, the image is divided into countless regularly arranged dots, that is, the continuous adjustment of image information into discrete dots. Image information. The larger the dot, the deeper the color of the performance, and the darker the layer; the smaller the dot, the lighter the color of the expression, and the brighter the level of representation, the size of the fixed space occupied by each dot is determined by the number of screen lines. For example, if the number of meshes is 150 lpi, there are 150 dots in the length or width of one inch. The location of network space and the size of outlets are two different concepts. For example, the meaning of C50% is that the size of outlets accounts for 50% of the location of outlets, and 100% refers to the total coverage of outlets, which is what is known in printing. "In the field," 0% has no outlets and only the dot space location, so no ink is printed on this place. Obviously, the larger the number of hanging nets is, the smaller the space occupied by the outlets is, and the more layers can be described, the more delicate they are. In fact, the level and color of the manuscript are reproduced through this method of hanging the net.
3. What is a continuous tone image? What is a halftone image?
A: Continuous-tone images usually refer to changes in tone from light to dark or dark to light on an image, and shades or shades are composed of the density of the imaged material particles per unit area. Such as the continuous adjustment of photographic color separation film, is composed of the density of metallic silver particles within the unit area; continuous adjustment of various color drawings is composed of various pigment particle densities per unit area, and the pigment particles per unit area are large. It is a dark tone, otherwise it is a light tone. Continually adjusting the depth of the image is infinitely variable.
Halftone usually refers to the change from light to dark or from light to dark on printed products after special processing, which is represented by the size of dot area. On the print screen, colors and shades are represented by dots. When observing the print screen, the dot area is large and the color is dark, which is called deep-tuning. The dot area is small and the color is light, which is called high-profile. Since the dots are spatially separated and discretely distributed, and because the number of stages of the screening is always limited, the level change of the image cannot be infinitely changed like continuous tone adjustment. The web image is a halftone image. Positive films, screen films, printed images, and the like like screens are halftone images.
4. Since the printed matter consists of halftone dots, why are we seeing a continuous image on the print?
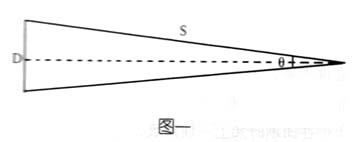
A: This is determined by the visual acuity of people. Visual acuity refers to the reciprocal of the two perspectives that the human eye can distinguish from the perspective of the human eye. The normal person's perspective is about 1 o. The minimum resolving distance of human eyes in figure 1 is the Dq·S1 o ×250mm 7.3×10 -2 mm at the clear vision distance. When the dot pitch in the print is less than this distance, the human eye cannot distinguish. Therefore, the image formed by the dots is treated as a continuous image.
(to be continued)Packing Bags, Packaging Bags, Food Packing Bags
Food Packing Bag Food Bags Co., Ltd. , http://www.nsabags.com